Thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU) are very versatile materials and are widely used in manufacturing storage tanks, inflatables, life jackets, medical devices and many more applications. Polyester and polyether are the two major varieties of polyurethane available along with a smaller class known as polycaprolactone. TPU can be further subdivided into Aliphatic and Aromatic TPU’s.
Both polyester urethane and polyether urethane are elastomers, a combination of the words elastic and polymer, which means they have elastic properties and have distinct polymer performance characteristics. Both types of composition have advantages and limitations and are appropriate for different applications. While Polyether TPUs offer good flexibility at low temperatures and hydrolysis, Polyester TPUs offer high chemical and oil resistance. Choosing the right grade of TPU with a good understanding of its chemical composition can greatly affect the functionality and lifespan of your product.
Polyurethanes is a multi-phase block co-polymer made by a chemical reaction between a polyol and disocyanate using a chain extender. The soft block (polyol) is responsible for the flexibility and elastomeric character of TPU while the hard block (disocyanate) gives the toughness and physical performance properties.
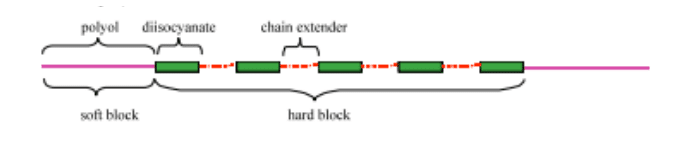
Small changes in the chemistry dictate how the TPU behaves, polyester TPU are made from polyols that contain ester groups, leading to excellent abrasion and chemical resistance and superior tensile strength and are also compatible with polar plastics like PVC. Polyether TPU’s made from polyols containing ether groups which impart excellent hydrolysis and microbial resistance along with outstanding low temperature resistance.
Aromatic and Aliphatic grades of TPU refer to changes made to the diisocyanate section of the TPU, where Aromatics are the most commonly available, having good abrasion resistance and tensile strength. Aliphatic grades have excellent clarity and won’t oxidize under UV radiation and don’t turn yellow, therefore they are used mostly in clear and/or outdoor applications.
Working with Ester and Ether Polyurethanes
When selecting the grade of TPU for an application, one should consider the environment where it will be used, operational and environmental temperatures, indoor or outdoor, chemical, and mechanical stress on the material, to what additional material does it need to adhere, are some of the key questions that will help narrow down the search. While polyester and polyether polyurethanes have similar durometer ranges, they have many major differences, below are some of the specific differences between the two:
Table of Contents
Polyester TPU main characteristics:
- Excellent Abrasion and Tear resistance
- Good tolerance to high temperature
- High elastic properties
- Superior Tensile and Mechanical Strength
- Improved Chemical Resistance
- Oil/Solvent resistance
Polyether TPU main characteristics:
- Low temperature flexibility
- Excellent Water resistance
- Good UV and wear resistance
- Antimicrobial and mold resistant
- Improved shock absorption
Changing the distribution of the hard and soft segments will impart different properties to the TPU, we will look at some of the Specific Properties for both types of TPU’s
Abrasion Resistance Properties
Urethanes have excellent abrasion resistance. They have far greater wear resistance than metals, plastics, and other rubbers. Abrasion resistance comes in two forms: sliding and impingement. Impingement refers to particles or things striking the urethane surface at a high angle, whereas sliding refers to scraping and rubbing abrasion.
- Polyester urethane has excellent resistance to sliding abrasion making it ideal for CIPP, dock seals, scraper blades.
- Polyether urethanes offer outstanding impingement abrasion resistance making it an excellent choice for sandblast curtains, bumpers, rafts.

Chemical, Grease, Fuel, Solvent, Water and Chemical Resistance
If the TPU is in a high humidity environment or is submerged or constantly exposed to water, polyether urethane is an excellent choice because of the hydrolytic stability. Polyether TPU also has good microorganism resistance.
Whereas if the product comes in contact with oils, fuels solvents, Polyester urethane provide excellent resistance from harsh chemicals making it ideal for CIPP liners, Storage tanks.
High and Low Temperature resistance
- Polyesters withstand high temperatures longer and are more resistant to heat aging.
- Polyethers are much less susceptible to dynamic heat build-up. That is why they are the choice for high-speed rollers where the rapid flexing creates heat.
- Polyether urethanes are less affected by cold temperatures compared to Polyester TPU.
Mechanical Properties
- Polyester based films will have higher tensile strength and higher cut and tear resistance when compared against Polyether films.
- Polyester is the choice for shock absorption and is used widely in vibration dampening applications.
- Polyether provides much higher rebound and therefore is the choice for skate wheels and high-speed rollers
From a price point, Polyether’s are more expensive than Polyester as the polyol that form the soft segment of a Polyether is generally priced higher on raw materials and is more complicated and difficult to produce, requiring advanced equipment. Also, being better in hydrolytic and low temperature resistance the demand is much higher for Polyether based TPU.
Both grades of TPU’s offer unique properties and selecting the correct material can become very challenging. At E2 we regularly work with a wide selection of TPU’s and have excellent long-standing relations with the major TPU suppliers of the world to offer solutions to your unique applications. To learn more about E2’s family of TPU coated fabrics, visit our website.
References:
- “Polyester vs. Polyether: What’s the Difference?” | https://psiurethanes.com/polyester-vs-polyether-whats-the-difference/
- “Difference between Polyester TPU and Polyether TPU”, https://www.sunmolin.com/news/knowledge/polyester
- “What’s The Difference Between Polyester and Polyether”Polyurethanes? (https://gallaghercorp.com/polyester-and-polyether/
- A guide to thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU), Huntsman
- 2019,” The difference between polyester & Polyether TPU”, Julier Technology Co. Ltd. https://www.custom-plastic-mold.com/info/difference-between-polyester-polyether-tpu-32332381.html









